Importance of Social Skills Development

Developing strong social skills is essential for children's overall development, and daycare environments play a crucial role in fostering these skills. The benefits of social skills development extend far beyond the daycare setting and have a lasting impact on a child's life.
Benefits of Social Skills
Social skills development leads to increased brain capacity, cognitive ability, and improved mental health [1]. When children engage in social interactions, they learn valuable skills such as communication, cooperation, problem-solving, empathy, and self-regulation. These skills enable children to navigate social situations successfully and form meaningful relationships.
Children who possess strong social skills tend to have more positive experiences in various aspects of their lives. They are more likely to have higher self-esteem, improved academic performance, and better emotional well-being. Additionally, children with well-developed social skills are better equipped to handle conflict, manage stress, and adapt to new environments.
Learning Environment in Childcare
Childcare settings create an ideal learning environment for social skills development. Children are exposed to a diverse group of peers and trusted adults, allowing them to learn how to interact, communicate, and collaborate with others. This exposure helps children develop skills such as sharing, taking turns, and resolving conflicts, which are crucial for successful social interactions.
In daycare, children have the opportunity to form attachments with caregivers, which fosters trust and a sense of security. This attachment provides a foundation for healthy social development, as children learn to rely on and seek support from trusted adults. Children also learn to navigate group settings, practice cooperation, and develop self-control. These experiences in daycare help children build resilience and adaptability, preparing them for future social interactions.
Ensuring that children are in the care of highly qualified educators is crucial for their social-emotional development. Educators with the necessary qualifications can provide a nurturing and supportive environment that promotes the development of social skills. Their expertise allows them to guide children in learning appropriate social behaviors, resolving conflicts, and developing a solid foundation of social-emotional skills.
In conclusion, social skills development is of utmost importance for children, and daycare settings offer valuable opportunities for this development. By engaging in social interactions and learning from educators and peers, children acquire the necessary skills to navigate social situations successfully. These skills have far-reaching benefits that positively impact various aspects of a child's life, including academic performance, emotional well-being, and future mental health.
Social Skills in Different Age Groups

At different stages of child development, social skills play a crucial role in shaping how children interact with others and navigate social situations. Let's explore the social skills exhibited by children in various age groups: infants (under one year), toddlers (one to three years), preschool children (three to five years), and early elementary children (six to eight years).
Infants (Under One Year)
Infants, younger than one year, demonstrate healthy emotional and social growth by actively trying to interact with adults, mimicking others' actions, and interpreting emotional expressions. They engage in social behaviors such as cooing, smiling, and making eye contact to establish connections with caregivers and other familiar faces. Separation anxiety is also common during this stage, as infants become attached to their primary caretakers and may exhibit distress when separated from them.
Toddlers (One to Three Years)
Toddlers, aged between one and three years, continue to develop their social skills by actively seeking independence and exploring their environment. They show affection, participate in group activities, and ask for what they want. Toddlers also engage in symbolic play, imitating others, and forming emotional attachments to certain items or comfort objects. They begin to develop a sense of self and display increasing verbal and nonverbal communication skills.
Preschool Children (Three to Five Years)
Preschool children, aged three to five, make significant strides in social skills development. They begin to understand what is appropriate or inappropriate behavior and learn to share and take turns. Preschoolers engage in cooperative play, where they interact and collaborate with their peers. They start interpreting emotions based on tone of voice and facial expressions and show concern for others. Preschoolers also demonstrate improved frustration tolerance and problem-solving skills.
Early Elementary Children (Six to Eight Years)
In the early elementary years, between six and eight, children continue to refine their social skills. They learn to lead and follow others, make choices regarding friendships, and play well with their peers. Early elementary children develop a sense of humor and show increasing concern for others. They become more self-critical, learn from their mistakes, and demonstrate a growing sense of responsibility for themselves and their belongings.
Understanding the social skills exhibited by children in different age groups is essential for educators and caregivers in daycare settings. By recognizing age-appropriate milestones, they can create appropriate environments and activities to support and enhance children's social development. To learn more about the importance of routine in daycare and its impact on child development, check out our article on the importance of routine in daycare.
Factors Influencing Social Skills
When it comes to developing social skills in daycare settings, several factors come into play. Educator qualifications, parent-teacher agreement, and teacher characteristics are all influential in shaping a child's social development.
Educator Qualifications
Highly qualified educators in daycare settings play a crucial role in fostering social-emotional skills in children. Their knowledge and expertise in child development enable them to create a conducive learning environment where children can develop a solid foundation of social skills. Educators with training in child development are better equipped to understand individual needs, provide appropriate guidance, and create learning opportunities that help children develop and practice social skills.
Parent-Teacher Agreement
Parent-teacher agreement regarding a child's social skills is an important factor to consider. Studies have found modest agreement between parents and teachers in various domains of social skills. This agreement allows for a holistic understanding of a child's social development, as parents and teachers bring different perspectives to the table. Communication and collaboration between parents and teachers are essential in ensuring a consistent approach to supporting the child's social growth.
Teacher Characteristics
The characteristics of teachers in daycare settings can significantly influence children's social skills. Studies have reported associations between parent and teacher ratings of children's social skills and various factors such as the child's birth rank, father's age, father's job, teacher's age, teacher's education, teacher's experience, and classroom environment. These findings highlight the importance of considering teacher characteristics when aiming to enhance social skills in children.
By paying attention to educator qualifications, fostering parent-teacher agreement, and considering teacher characteristics, daycare centers can create environments that promote the development of social skills in children. High-quality childcare with well-trained staff can effectively support children's social-emotional growth, providing them with the necessary skills for success not only in the classroom but also throughout their lives.
Social Skills Assessment
Assessing social skills is an important aspect of understanding a child's development in a daycare setting. It provides valuable insights into their interactions, communication, and ability to navigate social situations. In this section, we will explore different methods of assessing social skills, including parent and teacher ratings, gender differences, and social skill domains.
Parent and Teacher Ratings
To gain a comprehensive view of a child's social skills, it is necessary to gather input from both parents and teachers. Their perspectives provide valuable insights into the child's behavior and interactions in different environments. Studies have shown a modest agreement between parents and teachers in rating children's social skills, highlighting the importance of considering multiple perspectives.
By combining parent and teacher ratings, a more holistic understanding of a child's social skills can be obtained. This collaborative approach allows for a comprehensive assessment and helps identify areas where further support and intervention may be needed.
Gender Differences
When assessing social skills, it is important to consider potential gender differences. Research has shown that girls tend to display higher levels of cooperation, self-control, and total social skills from the parents' perspectives. However, from the teachers' perspectives, gender differences are less pronounced, except for a higher level of assertion in boys during the preschool years [4].
Understanding these gender differences can help educators and parents tailor their support and strategies to address the specific social skill needs of boys and girls. By recognizing and addressing these differences, a more inclusive and supportive environment can be created for all children in daycare.
Social Skill Domains
Assessing social skills involves evaluating various domains that contribute to a child's overall social competence. Common domains include cooperation, self-control, assertion, empathy, and self-esteem. Studies have reported that the majority of children exhibit moderate levels of social skills across these domains, as rated by both parents and teachers [4].
The following table provides an overview of the social skill domains and the average ratings from parents and teachers:
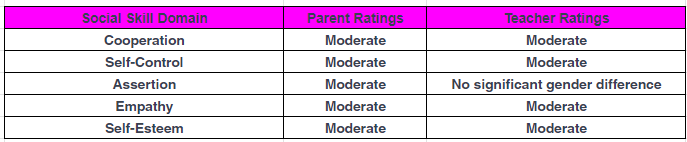
Figures courtesy NCBI
Assessing social skills within these domains allows educators and parents to identify specific areas of strength and areas that may require additional support. By focusing on these domains, targeted interventions and strategies can be implemented to enhance a child's social development in daycare.
Understanding how social skills are assessed is crucial for promoting healthy social interactions and relationships in daycare settings. By considering parent and teacher ratings, recognizing gender differences, and assessing social skill domains, educators and parents can collaborate to support children's social development effectively. Through targeted interventions, children can develop the necessary skills to navigate social situations, build positive relationships, and thrive in their daycare environment.
Strategies for Social Skills Development

To foster the development of social skills in children attending daycare, various strategies can be employed. These strategies aim to provide opportunities for children to learn and practice important social abilities. Here are three effective strategies commonly used in daycare settings:
Modeling Behavior
Modeling behavior is a powerful method for teaching children social skills. Adults, such as daycare educators, can serve as positive role models by demonstrating manners, teamwork, cooperation, and other desired social behaviors during interactions with children. Through observation, children can learn how to navigate social situations effectively and develop appropriate social responses. By consistently modeling positive behavior, educators create a nurturing environment that encourages the imitation and adoption of these skills.
Role-Playing Scenarios
Role-playing scenarios provide children with a safe and structured environment to practice their social skills. Educators can create scenarios that mimic real-life situations, such as sharing toys or resolving conflicts, and guide children through them. By actively participating in role-playing activities, children can learn how to communicate, take turns, problem-solve, and empathize with others. This hands-on approach allows children to develop a deeper understanding of social interactions and build the skills necessary for positive social relationships.
Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a valuable strategy to encourage the development of social skills in children. By offering praise and rewards for desired behaviors, educators can reinforce positive social interactions and encourage children to continue practicing these skills. Providing specific and genuine praise for actions such as sharing, using kind words, or displaying empathy reinforces the importance of these behaviors. Positive reinforcement helps children understand the value of social skills and motivates them to engage in prosocial behavior [5].
By implementing these strategies, daycare educators create an environment that supports the development of social skills in children. These strategies can be integrated into daily activities, group interactions, and structured lessons to provide consistent opportunities for children to learn and practice essential social abilities. As children engage in modeling behavior, role-playing scenarios, and receive positive reinforcement, they become equipped with the necessary skills to navigate social situations effectively and form meaningful connections with others.
For more tips on daycare management, check out our articles on daycare snack ideas for picky eaters, sensory play in daycare settings, handling behavioral issues in daycare, and the importance of routine in daycare.
Impact of Social Skills on Development
Developing social skills in daycare is not only important for creating strong relationships and positive interactions, but it also plays a crucial role in various aspects of a child's overall development. Let's explore the impact of social skills on academic performance, emotional well-being, and mental health.
Academic Performance
Research indicates that children with higher social competence tend to have better academic performance. When children possess well-developed social skills, they can form stronger friendships, collaborate effectively with peers, and communicate their thoughts and ideas with confidence. These skills contribute to a positive classroom environment, fostering a conducive atmosphere for learning and engagement.
By having the ability to work cooperatively in group activities, children with strong social skills can enhance their problem-solving skills, critical thinking abilities, and creativity. This can lead to improved cognitive development, increased brain capacity, and better academic outcomes.
Emotional Well-Being
Social skills development significantly influences a child's emotional well-being. Children with well-developed social skills tend to be happier, more motivated to learn, and have a positive attitude toward school. They are more likely to participate eagerly in class activities, demonstrate higher self-esteem, and exhibit better emotional regulation.
Having strong social skills allows children to develop positive relationships with their peers and educators, fostering a sense of belonging and support. This can lead to reduced feelings of isolation, loneliness, and the risk of developing mental health issues. By providing children with a strong foundation in social skills, daycare environments contribute to their overall emotional well-being.
Mental Health
The impact of social skills on mental health should not be underestimated. Children who lack social skills may experience difficulties in forming and maintaining relationships, struggle with adjustment at school, and exhibit behavioral problems. These challenges can have long-lasting effects on their mental health and overall development.
On the other hand, children who possess strong social skills tend to have better mental health outcomes. They are more likely to have positive social interactions, experience less loneliness, and have higher self-esteem. By instilling social skills in children early on in daycare settings, we can promote their mental health and well-being.
It is clear that social skills development in daycare has a profound impact on a child's academic performance, emotional well-being, and mental health. By nurturing these skills in a supportive and inclusive environment, daycare providers play a vital role in setting children up for success in various areas of their lives.
